题目描述:给定一个二叉树,返回它的 后序 遍历。
示例:
输入: [1,null,2,3]
1
2
/
3输出: [3,2,1]
方法一:迭代
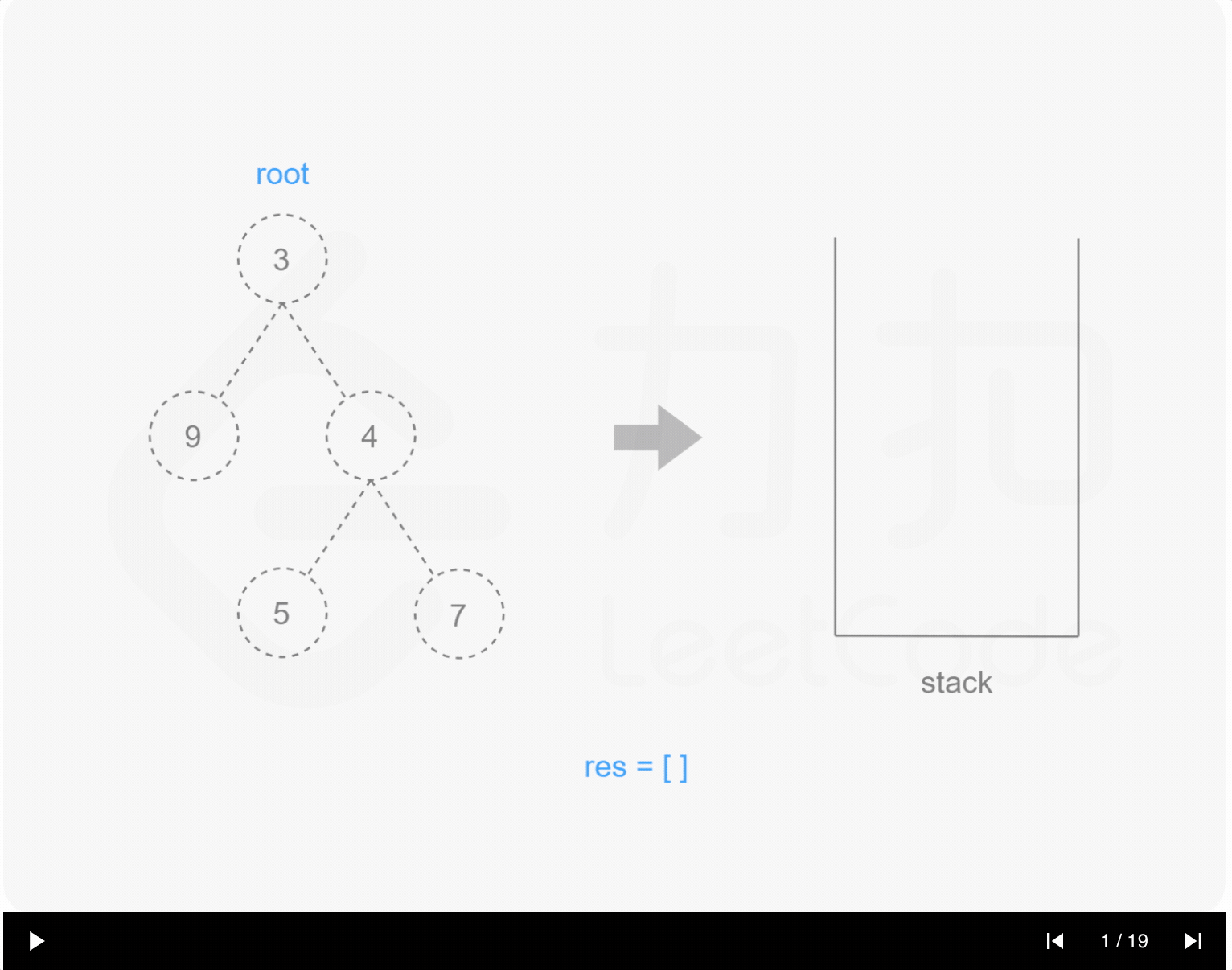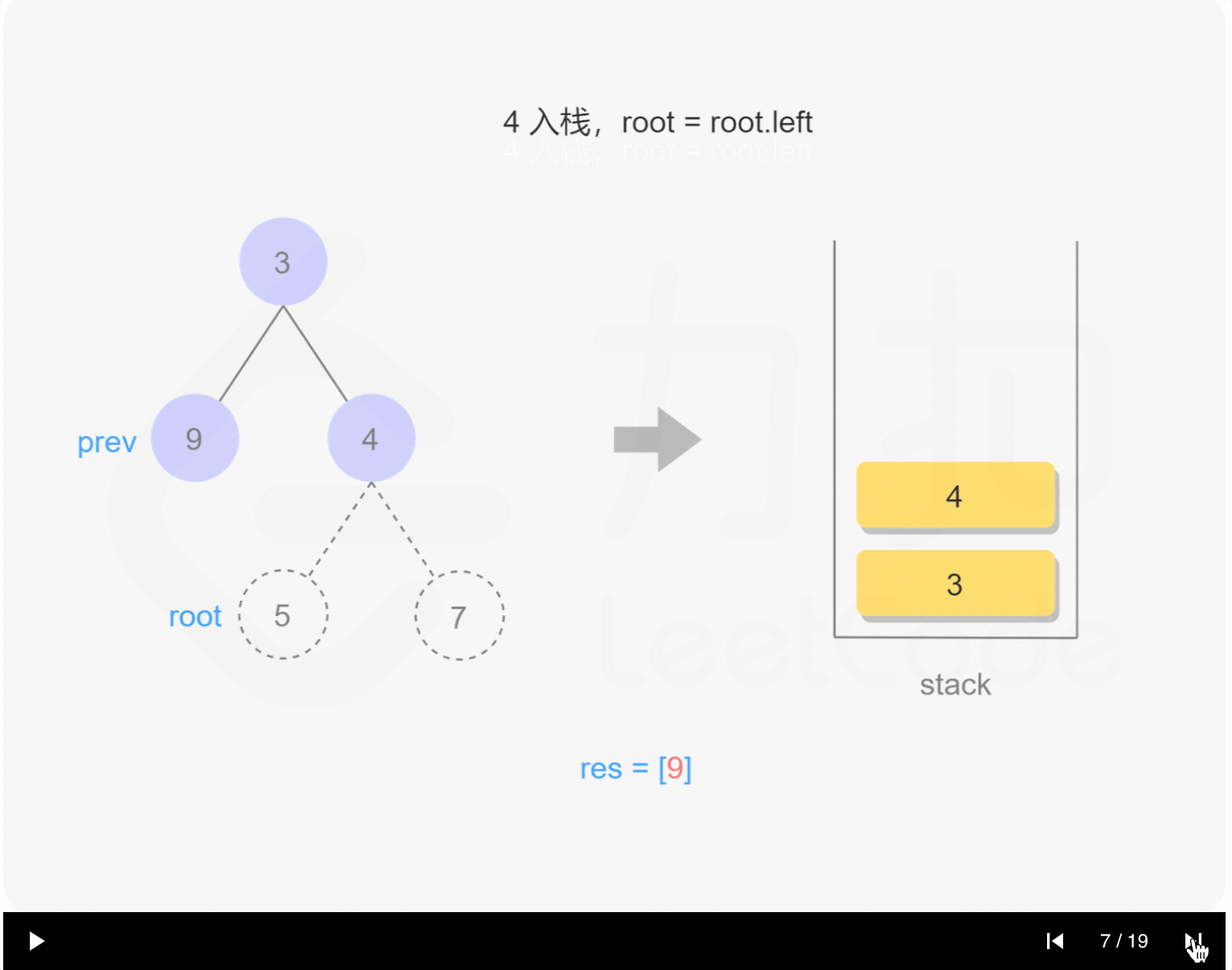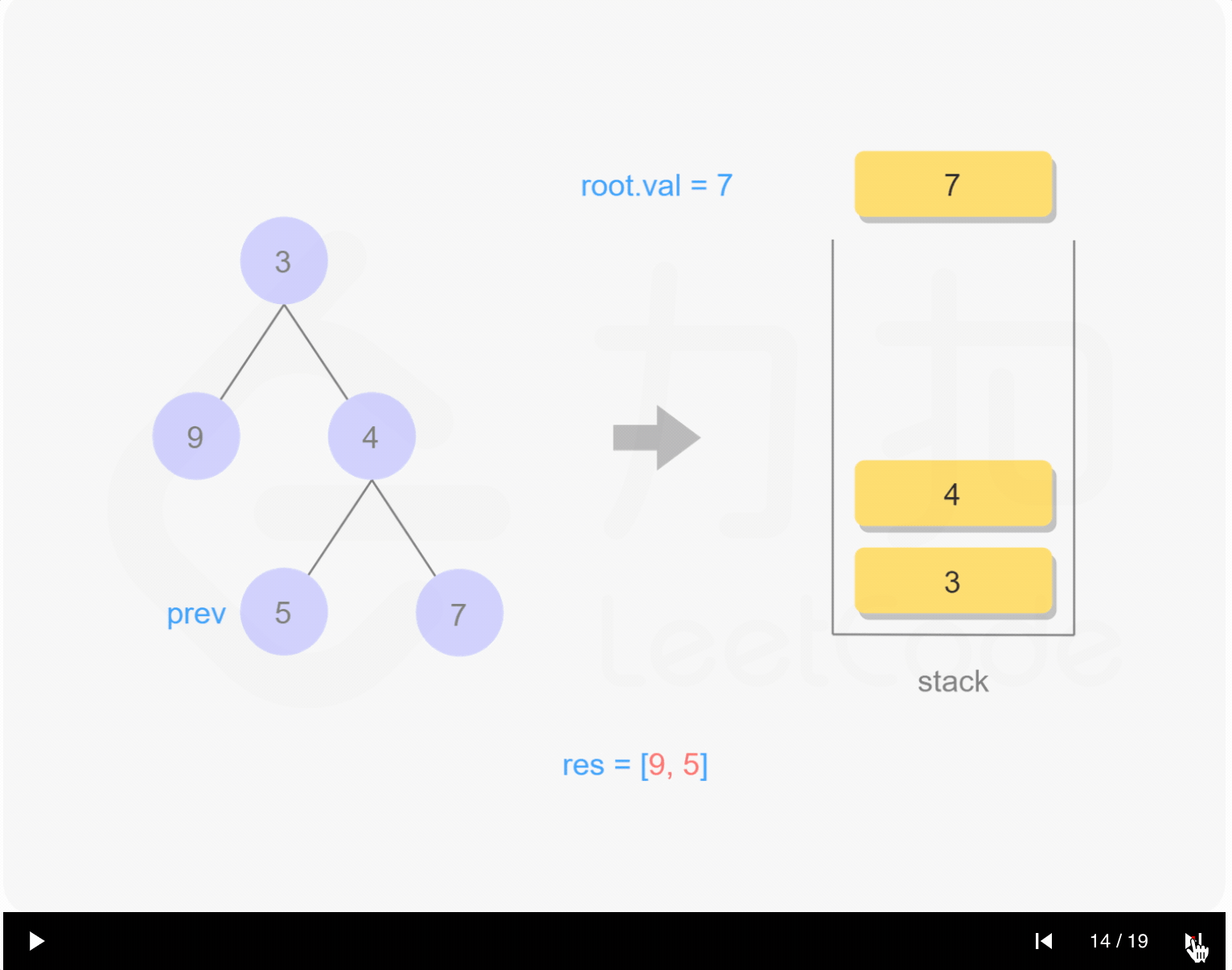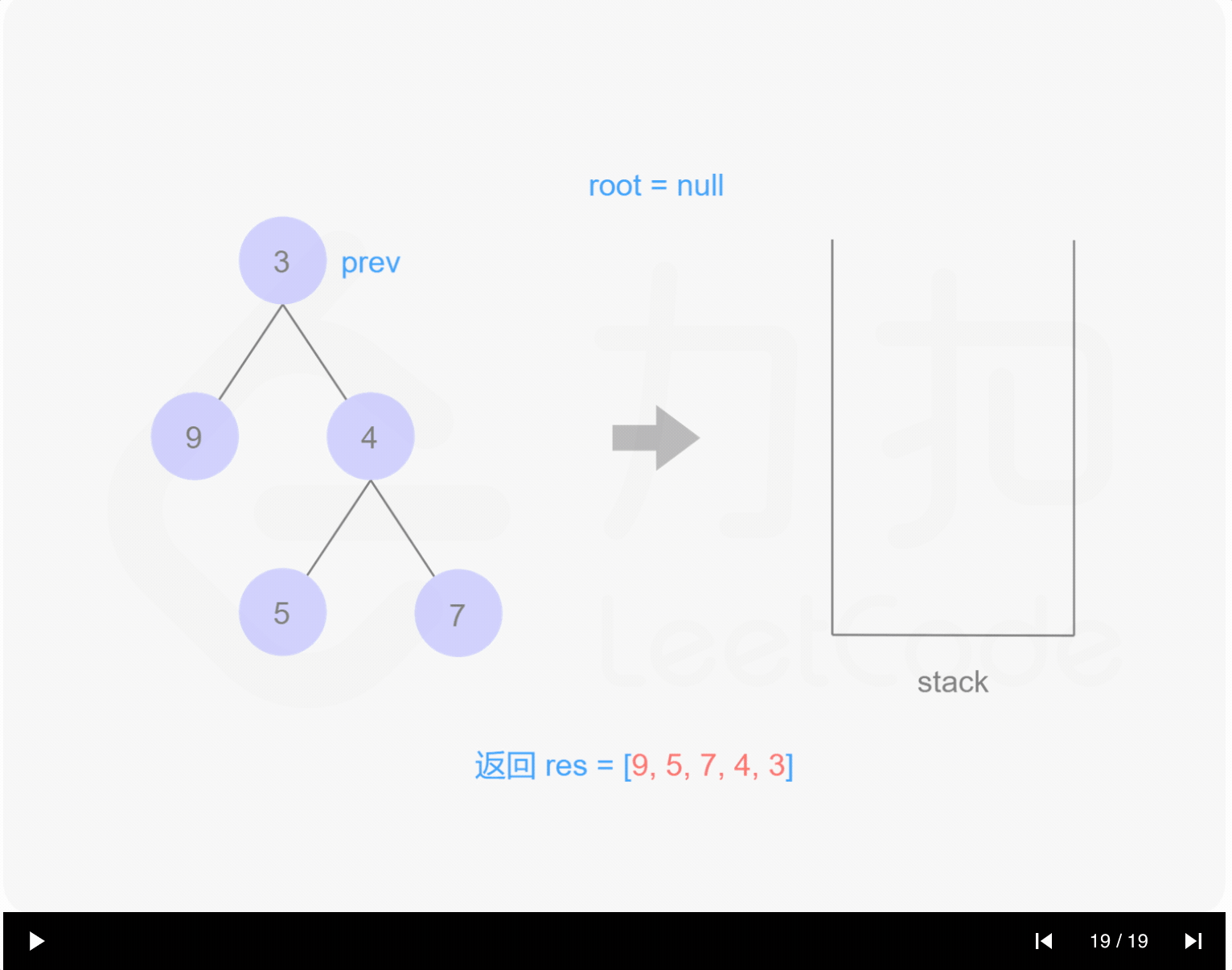
1 | /** |
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是二叉搜索树的节点数。每一个节点恰好被遍历一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(n),为迭代过程中显式栈的开销,平均情况下为 O(logn),最坏情况下树呈现链状,为 O(n)。
执行结果:通过
- 执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
- 内存消耗:36.6 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了68.52%的用户
方法二:递归
1 | class Solution { |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是二叉搜索树的节点数。每一个节点恰好被遍历一次。
空间复杂度:O(n),为递归过程中栈的开销,平均情况下为 O(logn),最坏情况下树呈现链状,为 O(n)。
执行结果:通过
- 执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
- 内存消耗:36.3 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了97.98%的用户